Literature

The Quran
by ThemePlus, used under 
I. Ancient Islamic Literature
Although the religion of Islam didn’t begin until the 7th century AD, the traditions and languages that influenced Islamic literature began many years before. Arabic and Persian are the two major languages that affected Islamic literature, and examples of the two languages can be viewed below.

A Sample of Arabic Text
by Inselleben, used under 

A Sample of Persian Text
by Garry Wilmore, used under 
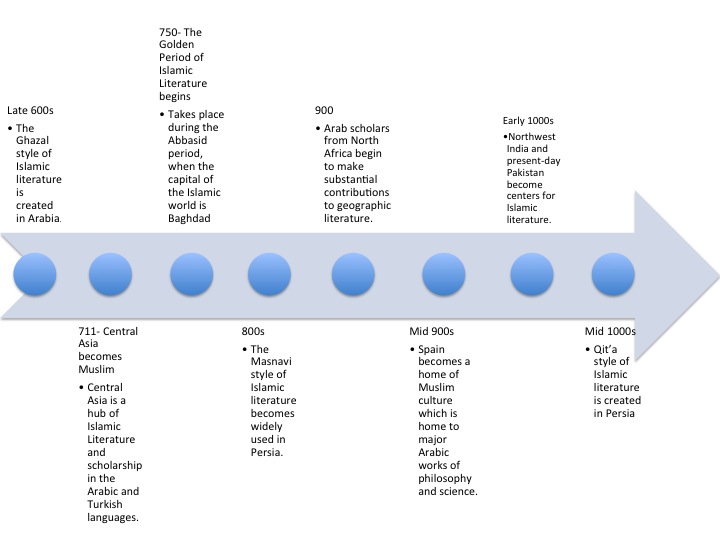
After the religion of Islam was formed, the Islamic culture spread across the East. With it, Islamic literature spread and developed. Below is a timeline of the major events after the founding of Islam that affected Islamic literature.
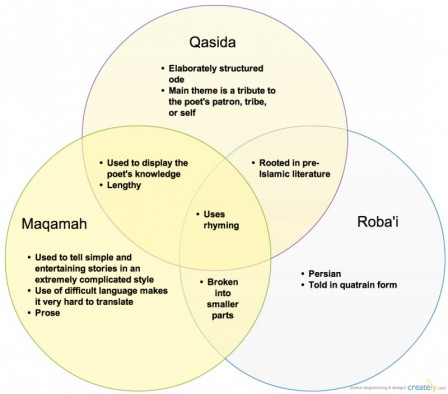
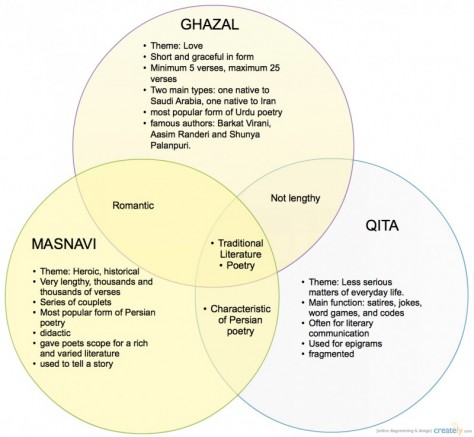
Six major types of ancient Islamic literature exist: the qasida, the ghazel, the qitah, the masnavi, and the roba`i. They are all poetic forms, and comparisons between the types can be viewed below.
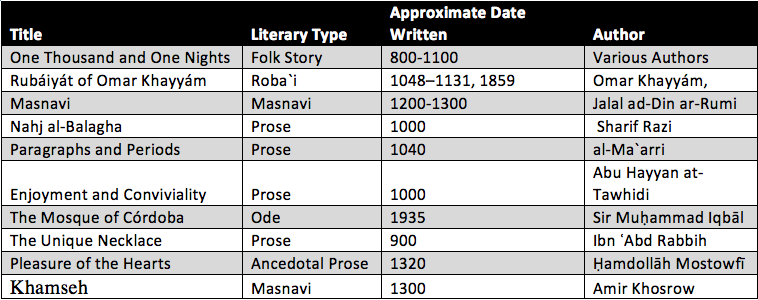
A table of major authors and works in ancient Islamic Literature:
A map containing major authors, and where they wrote their major works or most of their works of literature:
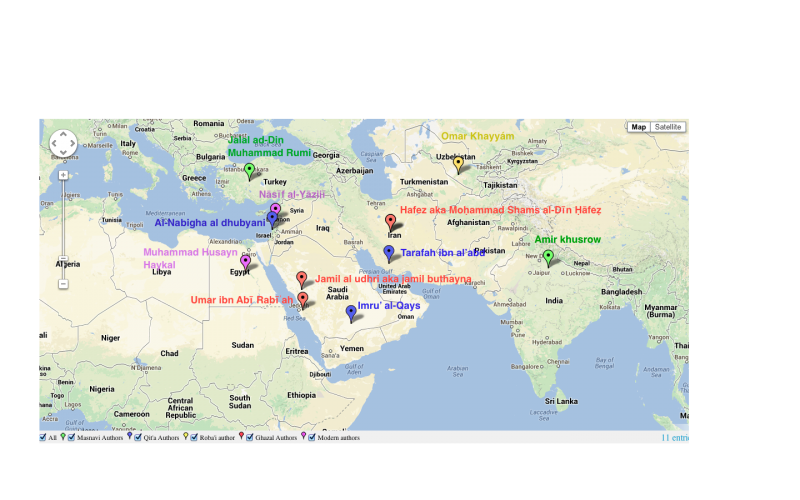
Red: ghazal authors
Blue: Qit’a authors
Green: Masnavi authors
Yellow: Roba’i authors
Purple: Modern authors
Islamic literature is perhaps best known for the book One Thousand and One Nights, which was written around the years 800-1100. It is a frame story, in which the wife, Scheherezade, of the ruler Jahshiyari, tells a different story every night for 1001 nights. The stories represent ancient folk tales of the Islamic regions.

An illustrated scene from One Thousand and One Nights
by Gabriel, used under 

A painting inspired by Hafez’s “Divan,” a Ghazal poem.
by Rhill, used under 

An image from an illustrated manuscript containing multiple ghazal poems, all reflecting love and longing.
by Coleman Barks, used under 
A book of examples of Qit’a poetry translated in English

An illustration of a masnavi poem about an arabic hero (left) and his lover (right).
by Horemachet, used under 
Video: Poetry reading of a Masnavi poem by author Rumi
II. Modern Islamic Literature
When the Europeans conquered (and subsequently divided) the Arab nations, they brought with them all kinds of new literature. The Sykes-Picot agreement in the early 20th century divided the region into 4 “zones” controlled by different countries.
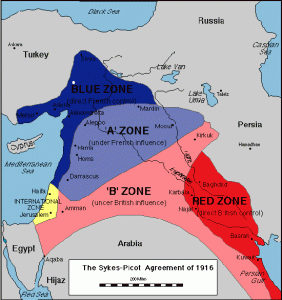
Sykes-Picot 1916
by Trey Menefee, used under 
The dominance of the European nations meant the qaṣīdah, maqāmah, and other genres refined in the premodern period gave way to the play, the novel, the short story, and free verse.
Prior to the Sykes-Picot agreement, there was an underground translation movement, which translated European, Asian, and American novels, poems, and periodicals to Arabic. Zaynab by Muhammed Husayn Haykal is considered by many to be the first Arabic novel. Zaynab was published in 1913 and originally was intended to be a short story. Instead, it ended up becoming a full length, three-part novel. This work was the first, and most notable example of the rising short story movement.
Type of writing was not the only thing to change from the European influence. Instead of focusing solely on religious teachings and beliefs, some authors took to writing as a way to criticize social, economic, or political issues. The first example of this was actually a set of maqamat written in the late 17th century. This set of poems, were originally written with religious context, were now used as a template to criticize social issues in Egypt and throughout the arabic world.
References:
Cornell, U. (n.d.). Islamic literature. Retrieved from http://www.library.cornell.edu/colldev/mideast/islamlit.htm
ghazal. (2013). In Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Islamic literature. (2013). In Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved from http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/295723/Islamic-literature
Kanda, K. (n.d.). Retrieved December 10, 2013, from http://www.mushaira.org/history.php”Muslim Journeys | Item #190: ‘Arabic Literature’ from Oxford Islamic Studies Online”, December 10, 2013 http://bridgingcultures.neh.gov/muslimjourneys/items/show/190.
Persian literature. (2013). In Encyclopaedia Britannica.