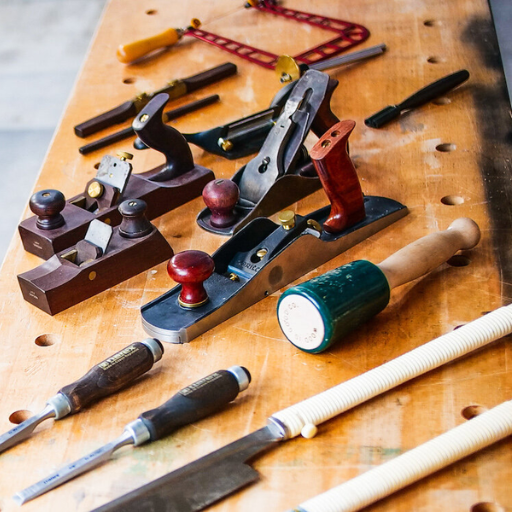
When it comes to tackling DIY projects, woodworking, or professional construction tasks, having reliable hand tools is non-negotiable. But with so many brands on the market, how do you know which manufacturers truly deliver unmatched quality and performance? This guide is here to take the guessing out of the equation. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a novice craftsman, we’ll explore industry-leading hand tool brands renowned for their durability, innovation, and craftsmanship. From trusted names with decades of excellence to cutting-edge newcomers redefining the tools of the trade, this article will help you discover the best options for your needs.Click here to read more
What Are the Best Hand Tool Brands?

What Are the Best Hand Tool Brands
- DeWalt – Known for its durable and versatile tools, DeWalt is trusted by professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike for its dependable performance.
- Stanley – A legacy brand recognized for its affordable yet reliable tools, perfect for general home and professional use.
- Craftsman – With a strong reputation for quality and a lifetime warranty on many tools, Craftsman remains a top choice for many users.
- Milwaukee – Famous for its cutting-edge technology and robust designs, Milwaukee caters primarily to professionals who demand high performance.
- Klein Tools – Specializing in tools for electrical work, Klein Tools is a leader in providing precision and durability for specific trades.
Exploring Top Hand Tool Manufacturers
- Stanley Black & Decker
One of the most recognized names in the hand tools industry, Stanley Black & Decker offers a wide range of tools catering to professional tradespeople and DIY enthusiasts. Known for their durability and innovative features, their brands—such as Stanley and DeWalt—are favored for carpentry, construction, and maintenance tasks.
- Snap-on
Highly regarded among automotive and professional mechanics, Snap-on tools are renowned for their precision engineering and premium materials. While they come with a higher price tag, they are designed to withstand rigorous daily use and offer exceptional performance.
- Milwaukee Tool
Milwaukee is synonymous with advanced technology and robust design. They specialize in creating power tools and hand tools that cater to professionals demanding high efficiency and reliability. Their toolsets often integrate ergonomic designs and innovative solutions for demanding applications.
The Role of Tool Brands in Quality
Tool brands play a critical role in ensuring the quality, durability, and performance of tools used by both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. Renowned brands invest heavily in research and development to produce innovative designs that enhance efficiency and precision. These brands prioritize the use of high-grade materials, advanced manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control processes to ensure their tools can withstand demanding applications. Furthermore, top tool brands often provide warranties, responsive customer support, and ensure compatibility with a wide range of accessories, solidifying trust among their users. By consistently delivering products that exceed expectations, these brands set industry standards and empower users to perform their tasks with confidence and accuracy.
Why Choose High-Quality Hand Tools?
High-quality hand tools are essential for ensuring efficiency, reliability, and safety across various tasks. They are designed with superior materials and craftsmanship, offering enhanced durability and precision compared to lower-grade alternatives. Investing in premium hand tools reduces the risk of tool failure, minimizing downtime and costly replacements. Additionally, these tools often incorporate ergonomic designs, promoting user comfort and reducing strain during extended use. Professionals and hobbyists alike benefit from the consistent performance, precision, and long-term value provided by high-quality tools, making them a smart and cost-effective choice.
How to Choose the Right Hand Tool for Your Needs

How to Choose the Right Hand Tool for Your Needs
- Purpose
Identify the specific task you need the tool for. Different tools are designed for different purposes, so selecting one suited to the job ensures efficiency and effectiveness.
- Quality
Opt for tools made with durable materials such as high-grade steel or carbon composites. High-quality tools usually last longer and deliver better performance.
- Ergonomics
Look for tools with comfortable grips and ergonomic designs. These reduce strain and make extended work periods more manageable.
- Size and Fit
Choose a tool that matches the size of the work area and fits comfortably in your hand for precise and safe handling.
- Brand Reputation and Reviews
Trust reputable brands with a history of producing reliable tools. Reading user reviews can also provide insights into performance and durability.
Understanding Types of Hand Tools
- Cutting Tools
Examples include saws, scissors, and utility knives. These tools are designed to cut through materials such as wood, plastic, or metal with precision.
- Fastening Tools
Tools like screwdrivers, wrenches, and pliers fall under this category. They are used for gripping, tightening, or loosening bolts, nuts, and screws, making them critical in assembly and repair tasks.
- Striking Tools
Hammers, mallets, and chisels are popular striking tools. They are used for driving nails, shaping materials, or breaking objects, depending on the project.
- Measuring Tools
Tape measures, levels, and calipers ensure accuracy during a project. These tools help maintain precision in building, cutting, or assembling.
- Specialty Tools
Purpose-specific tools such as wire strippers, hand planers, and pipe cutters are tailored for niche tasks, offering efficiency in specialized applications.
Matching Tools for Home and Professional Use
- Power Tools
Power tools like cordless drills, circular saws, or sanders are invaluable for home renovation and large-scale professional construction. Opt for models with adjustable settings to handle both intricate and demanding tasks.
- Hand Tools
High-quality hand tools, including hammers, wrenches, and screwdrivers, are fundamental for precise work in any environment. Look for tools made from durable materials such as chrome-vanadium steel to last through frequent use.
- Specialty Tools
For those handling plumbing, electrical, or woodworking tasks, specialty tools like pipe cutters, voltage testers, or hand planers bridge the gap between basic home improvement and professional-grade work. Investing in these tools ensures you’re prepared for more specific challenges.
Essential Tools You Need in a Tool Box
Building a well-rounded tool box is crucial for tackling a variety of projects with ease. Below are the essential tools that should be a part of every tool box:
- Measuring Tools
A reliable tape measure is indispensable for ensuring precision in any project, whether it’s hanging pictures or cutting materials to specific sizes. A spirit level is also a must-have for achieving perfect alignment.
- Cutting Tools
Sharp, high-quality cutting tools like a utility knife and a handsaw are fundamental for both quick adjustments and larger woodworking projects.
- Fastening Tools
Include a set of screwdrivers (both flathead and Phillips) and a claw hammer in your tool box. These tools are used for assembling furniture, hammering nails, or loosening screws.
- Wrenches and Pliers
A set of adjustable wrenches and a pair of locking pliers are crucial for gripping, holding, and turning objects, especially for plumbing or mechanical work.
- Power Tools
For more advanced projects, consider adding a cordless drill with a variety of drill bits. It speeds up tasks like installing shelves or building furniture.
- Safety Gear
Don’t forget safety essentials like work gloves, safety goggles, and a dust mask to protect yourself during any project.
What Makes Top Quality Hand Tools Stand Out?

What Makes Top Quality Hand Tools Stand Out
Top-quality hand tools stand out due to their durability, precision, and ergonomic design. They are typically made from high-grade materials, such as hardened steel, ensuring they can withstand repeated use without degrading. Precision manufacturing guarantees accurate performance, allowing for reliable results in any project. Additionally, ergonomic handles and thoughtful designs reduce strain, making them comfortable to use over extended periods. Investing in high-quality tools not only enhances efficiency but also ensures safety and long-term cost savings.
Features of High-Quality Hand Tools
- Durable Construction
High-quality hand tools are crafted from robust materials like chrome vanadium steel or stainless steel, offering exceptional durability and resistance to wear, corrosion, and heavy use over time.
- Ergonomic Design
These tools prioritize user comfort, featuring non-slip, ergonomic grips that reduce hand fatigue and strain, even during extended use, ensuring a safe and productive experience.
- Precision Engineering
Advanced manufacturing processes ensure that high-quality tools provide superior accuracy, tight tolerances, and reliable performance, making them ideal for detailed and demanding tasks.
- Versatility and Functionality
Premium hand tools often incorporate multi-functional capabilities, combining several uses into a single device, which enhances their practicality across diverse applications.
- Longevity and Repairability
They are designed to last, often coming with warranty offers and options for repair, providing a sustainable and cost-effective choice for both professionals and hobbyists.
The Hand Tool Industry and Innovation
The hand tool industry continues to grow and evolve, driven by technological advancements and a focus on efficiency. Modern innovations are centered around creating tools that are more ergonomic, durable, and versatile, addressing the diverse needs of both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. Smart tools equipped with sensors and connectivity features represent the next frontier, enabling precision and increased productivity. Sustainability is another major focus, with manufacturers exploring eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce environmental impact. These developments reflect the industry’s commitment to balancing performance, user-friendliness, and sustainability in an increasingly competitive market.
Commitment to Quality: What to Look For
When evaluating tools, there are several key factors to ensure you’re investing in quality. First, consider the durability of materials—high-quality tools are often made from robust materials like hardened steel or heavy-duty composites, designed to withstand regular use without compromising performance. Next, examine ergonomics to ensure the tool is comfortable to use for extended periods; look for features such as non-slip grips and well-balanced designs. Brand reputation is another reliable indicator—trusted manufacturers with a history of positive reviews often provide better warranties and after-sales support, reflecting confidence in their products. Additionally, assess the availability of innovative features, such as digital displays or smart connectivity, which enhance precision and usability.
Who Are the Leading Hand Tool Manufacturers?

Who Are the Leading Hand Tool Manufacturers
Several companies stand out as leading manufacturers of high-quality hand tools. Stanley Black & Decker is renowned for producing durable tools under trusted brands like Stanley and DeWalt. Snap-on is another industry leader, offering premium tools favored by professionals for their reliability and craftsmanship. Klein Tools specializes in tools for electricians and tradespeople, with a strong focus on quality and performance. Additionally, brands like Makita and Husky are widely recognized for providing a range of tools suited for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. These manufacturers prioritize innovation, durability, and user satisfaction, making them trusted choices in the industry.
Spotlight on German Hand Tool Manufacturers
German hand tool manufacturers are renowned worldwide for their precision, quality, and engineering excellence. Brands such as Wiha, WERA, and Felo stand out as leaders in the industry, consistently delivering tools that professionals and enthusiasts trust.
Wiha Tools focuses on creating ergonomic, durable, and high-performance screwdrivers, pliers, and insulated tools. Their products cater to electricians and engineers seeking unparalleled reliability. WERA, another highly respected brand, is celebrated for its innovative tool designs, including its Kraftform screwdriver handles and advanced ratchets. Meanwhile, Felo specializes in producing screwdrivers and bit sets designed for exceptional torque and efficiency, with a strong commitment to sustainability and precision manufacturing.
Innovators: Klein Tools and Dewalt
Klein Tools has been a leader in hand tools for over 165 years, renowned for its dedication to professional-grade quality, particularly in electrical and utility applications. Their tools, such as pliers, screwdrivers, and wire cutters, are designed to withstand heavy use while offering ergonomic comfort and precision. Klein’s focus on innovation and durability has made it a trusted name among electricians and technicians worldwide.
Dewalt, on the other hand, is synonymous with high-performance power tools and accessories. Known for robust construction, Dewalt designs its tools to meet the demands of construction and industrial professionals. The brand’s cordless systems, featuring advanced lithium-ion battery technology, offer unparalleled mobility and efficiency. With an ongoing commitment to innovation and jobsite solutions, Dewalt continues to push the boundaries of tool technology, making it a favorite for heavy-duty applications.
Exploring the Apex Tool Group and Craftsman
The Apex Tool Group is a leading manufacturer of professional hand and power tools, catering to industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction. Renowned for their reliability and precision, Apex’s brands include Crescent, GearWrench, and Weller, offering a diverse range of products from wrenches to soldering tools. Apex focuses on delivering high-performance tools that meet the rigorous demands of professionals, supported by continuous innovation and engineering excellence.
Craftsman, on the other hand, is a household name synonymous with durability and versatility. Known for producing hand tools, power tools, lawn equipment, and storage solutions, Craftsman has been a trusted brand for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts since 1927. With a lifetime warranty on many of its tools, Craftsman emphasizes quality and customer satisfaction. Over recent years, the brand has modernized its offerings with advancements in design and functionality, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of users.
Building a Comprehensive Hand Tool Collection

Building a Comprehensive Hand Tool Collection
Building a reliable hand tool collection starts with a focus on versatility and durability. For general use, the following tools are indispensable:
- Hammer – Ideal for driving nails, removing fasteners, and other basic tasks.
- Screwdrivers – A set with multiple sizes and types (flathead and Phillips) ensures compatibility with various screws.
- Wrenches – A mix of adjustable wrenches and combination wrenches allows for handling a range of bolt sizes.
- Pliers – Include needle-nose, slip-joint, and locking pliers for gripping, bending, and cutting tasks.
- Tape Measure – A durable, retractable tape measure is vital for accurate measurements.
- Utility Knife – Perfect for cutting materials like cardboard, rope, or plastic.
- Level – Ensures precision when installing shelves, frames, or other items.
Choosing the Right Tool Sets for Your Needs
When selecting the ideal tool set, it’s essential to align your choice with your specific projects and skill level. For beginners, look for versatile sets that include essentials like screwdrivers, pliers, hammers, and wrenches. These kits provide a strong foundation for basic home repairs and maintenance tasks. Intermediate and advanced users should consider specialized tool sets tailored for woodwork, electrical work, or automotive projects. Pay attention to material quality—hardened steel and ergonomic grips ensure durability and ease of use. Brands offering lifetime warranties are a plus, as they guarantee long-term reliability for your investment.
Creating a Range of Tools for Every Task
When building a versatile range of tools, start with essentials such as screwdrivers, pliers, a tape measure, and a high-quality hammer. These are fundamental for tackling most basic tasks. For more specialized needs, consider power tools like a cordless drill, circular saw, or impact driver, ensuring they meet safety standards and offer durability. Opt for multi-purpose tools that can adapt to various tasks, reducing the need for redundancies.
Pay attention to material quality—chrome vanadium steel is widely recommended for hand tools due to its strength and resistance to corrosion. For organization, modular toolboxes and labeled compartments can make locating and transporting tools easier while reducing clutter. Top-rated tools often balance performance, cost, and warranty support.
Advantages of a Wide Range of Hand Tools
A wide range of hand tools offers numerous advantages, ensuring versatility and ease in tackling various tasks. First, having diverse tools allows for precision and efficiency, as specific tools are designed to perform distinct functions, reducing the risk of damage to materials or improper repairs. Second, it promotes safety by minimizing the chances of using inappropriate tools that could lead to injuries. Third, access to a comprehensive collection ensures readiness for both routine maintenance and unforeseen challenges, saving time and effort. Additionally, investing in quality hand tools typically results in long-term cost-effectiveness due to their durability and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What should I consider when choosing hand tools from the best brands?
A: When choosing hand tools, consider quality and durability, the brand’s reputation, the selection of hand tools they offer, and whether they have a variety of tools to meet your specific needs. Opt for brands known for producing high-quality hand tools that ensure reliability and performance.
Q: Which are the top brands known for high-quality hand tools?
A: Some of the top brands known for high-quality hand tools include Irwin Tools, Craftsman Tools, and other reputable hand tool companies. These brands are recognized for their quality and innovation, offering a wide range of tools for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Q: What makes Irwin Tools a preferred choice for hand tools?
A: Irwin Tools is a preferred choice due to their commitment to producing tools with quality and durability. They offer a variety of hand tools, including screwdrivers, pliers, and wrenches, which are essential for both professionals and hobbyists. Their tools are known for their reliability and performance on the market.
Q: How do industrial tools differ from regular hand tools?
A: Industrial tools are designed for heavy-duty use and are often built to withstand rigorous conditions, making them suitable for industrial settings. They are typically more robust than regular hand tools and are used in professional and industrial applications where high performance is critical.
Q: Why is tool storage important when dealing with a variety of hand tools?
A: Proper tool storage is crucial to keep your tools organized, protected, and easily accessible. It helps prolong the life of your tools by preventing damage and loss, ensuring that you can maintain the quality and durability of your selection of hand tools.
Q: What are the benefits of using ratcheting tools?
A: Ratcheting tools offer the advantage of efficiency and ease of use. They allow for continuous motion in one direction without removing the tool from the fastener, making them ideal for tight spaces and improving productivity. They are a favorite among professionals looking for high-quality hand tools.
Q: How can I ensure I’m choosing the best tool for my needs?
A: To ensure you’re choosing the best tool, assess your specific needs and tasks, research different brands, and consider tools that offer quality and innovation. Look for brands that have a reputation for producing high-quality hand tools and offer a variety of options suited to your requirements.
Q: Are there all-in-one tool solutions available from top brands?
A: Yes, many top brands offer all-in-one tool solutions that combine multiple functions in a single tool. These are particularly useful for versatility and convenience, allowing you to tackle a variety of tasks without the need for multiple individual tools.
Q: What should I look for in a brand offering a wide range of hand tools?
A: Look for a brand that emphasizes quality and durability, offers a comprehensive selection of hand tools, and has a strong reputation in the industry. It’s essential that they provide tools that cater to both general and specific tasks, ensuring you have the hand tools you need for any project.