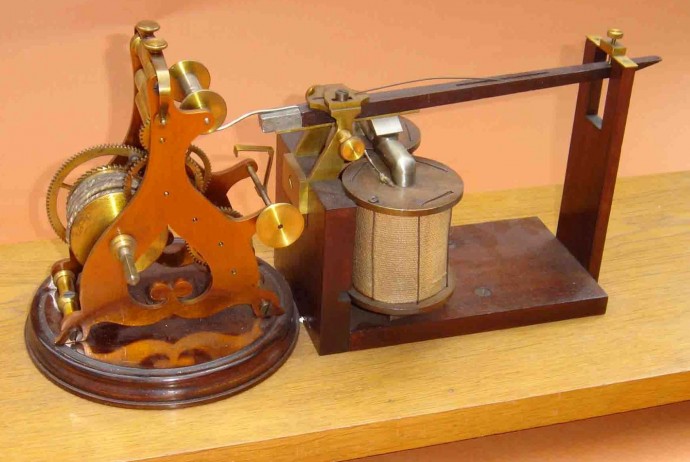
The Telegraph
By: Lauren Daniel
The industrial revolution was all about replacing manual labor with machine labor. One of the inventions that was developed during the revolution was the telegraph. Telegraph is a Greek word that when broken down means “a written message sent from afar”. The telegraph was a way for people to send messages and news across the world using electricity. This way of communication was faster than anything that had ever been invented up to that point in history.
By the 1830’s and 1840’s, an electrical type of telegraph was invented by Samuel Morse. This telegraph was considered the start of long-distance communication and would change the world forever. The telegraph worked by sending codes made up of short and long pulses of electrical currents, which we know today as Morse Code. Morse Code is a set of dots and dashes that each represent a letter of the alphabet. In order to send messages, the operator would simply have to press a switch which would send a current via wire to the receiving telegraph. The receiving operator would then be able to interpret the dots and dashes that were made on the piece of paper. After awhile the operators became so familiar with the sounds each letter and number would make that they could simply translate by ear and could eliminate the use of the paper. (Telegraph and Telephone).
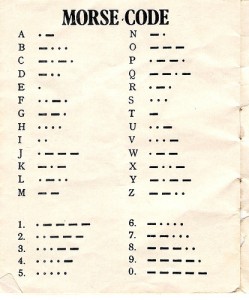
A Morse Code Chart 
This work (Morse Code, by Anthony Cox), identified by Lauren Daniel, is free of known copyright restrictions.
In 1844, the first telegraph message was sent across the United States. Morse, who was in Washington D.C. sent a code to his assistant in Baltimore that read, “What hath God wrought!” Years later in 1866, a telegraph line was made to go across the Atlantic Ocean so that different countries and continents could communicate using this system. Starting in 1876, when Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, a much easier and faster way to communicate, the telegraphs were not the only means of long-distance communication.
Before the invention of the telegraph in the early 19th century, communicating over long distances was difficult and had many limitations. Methods such as smoke signals and drums were used to relay information, and these methods were often unreliable. That is why the telegraph is so revolutionary; it had the ability to not only send messages across a country, but across continents. It changed the course of communication and paved the road for new methods in the future as well (Morse Code and the Telegraph).
If you want to find out more about the invention of the Telegraph, check out the History Website!
Citations:
Morse Code and the Telegraph. (n.d.). Retrieved April 8, 2014, from History: http://www.history.com/topics/inventions/telegraph
Telegraph and Telephone. (n.d.). Retrieved April 16, 2014, from Know It All: http://www.knowitall.org/kidswork/etv/history/telegraph/
Morse Code [image]. (n.d.). Retrieved April 16, 2014, from Flickr: https://www.flickr.com/photos/coxar/310256170/in/photolist-tq9mj-7G94qm-aQ9H5-6p5FYG-8xMcDf-FEzZ1-2rA36-5jQxdQ-4oDRaV-4ctVpa-6u1uVu-3f4R3X-vLQdu-5jgwr-d3HCsw-bAoAAd-ccwA7s-4DNsH9-7zeveS-guF4hi-5d9MuV-5WHKgk-6jchje-5dbzDR-5z2KXV-5dfUvC-5dfUyW-doxY9t-5E1tdC-8NKYyr-8NKZcR-57pcKr-5rwDWF-5EkJ3s-e7LeVz-kU9Dbt-3hH2TL-4JRzgb-eUiF4p-4RD6CE-2btBF1-8NFM14-e7S77b-4JRzkJ-dbPXiX-P5BNh-5EkJ3q-5uye5m-4NZTmG-duu7AyURL
