Want more A’s? Get more Zzzz’s
November 24, 2015
For many 18-22 aged college students sleep is towards the bottom of priorities and is often the first thing to get neglected. Students have classes, homework, sports teams, work, Greek life, social lives and many other commitments that come before sleep! However, according to the National Sleep Foundation sleep is as vital as the air we breathe, the water we drink and the food we eat. It is recommended that collaged aged students get 7-9 hours of sleep per night but the average college student only gets 6-7 hours. Lack of sleep can seriously impact your health, mood, GPA and safety. You are not only more likely to fall asleep in your 8am classes you are also more likely to do worse on exams. Therefore before you choose to pull an ‘all-nighter’ studying for that final exam, or have a few drinks with your friends when you have work at 7am the next day, think about the unhealthy extra strains you are putting on your body and mind. After a goods night sleep you are more likely to be able to concentrate better, problem solve more efficiently and increase your memory therefore assisting in your ability to gain an A on that big final exam!
Negative Effects
- Lower your GPA. Including your ability to learn, listen, concentrate and solve problems.
- Break out in pimples. Lack of sleep can contribute to acne and other skin problems.
- Mood swings. Can lead to aggressive or inappropriate behavior such as yelling at your friends or being impatient with your teachers or family members.
- Weight gain. Can cause you to eat too much or eat unhealthy foods like sweets and fried foods.
- Illness. Increases your chances of getting a cold or flu due to a weaker immune system.
- Dangerous activities. Increases the chance of injury due to not using equipment safely or driving drowsy.
NOT so fun fact
When you are sleep deprived, you are as impaired as driving with a blood alcohol content of .08%, which is illegal for drivers in many states. Drowsy driving causes over 100,000 crashes each year. Recognize sleep deprivation and call someone else for a ride.
Only sleep can save you!
Sleep Disorders
Narcolepsy – Tendency to fall asleep during day time hours and falling immediately into a deep REM sleep. There is no cure but can be controlled using medicine.
Insomnia – Lack of quality and quantity of sleep. Treated by determining the cause of the problem and then changing your habits.
Restless legs syndrome – Having a strong urge to move your legs after going to bed causing problems falling asleep and waking up often. Treated by lifestyle changes and medicine.
Sleep apnea – When you stop breathing during your sleep repeatedly during the night. Treated by changing your lifestyle and wearing an oxygen mask during sleep.
Solutions
- Make sleep a priority. Keep a sleep diary.
- Nap smart! No more than 1 hour or after 3pm
- Make your room a sleep heaven. Keep it cool, dark and quiet.
- Your bed is only for sleeping. No studying or watching TV.
- Establish a routine. Try to go to bed and wake up every day around the same time.
- Don’t sleep in all weekend. This can shock your body and negativity effect your routine.
- Turn it off! Avoid TVs, computers and phones.
- Try taking a bath or reading a book just before bed to relax the mind and body.
- Keep a ‘to do’ list. So you don’t stay up all night worrying or stressing.
- Eat a little snack. Don’t eat too much before bed but have a little snack so your not hungry.
- Do some sort of physical activity throughout the day but try to avoid exercise just before bed.

Resources
https://www.uhs.uga.edu/documents/Sleep-Diary.pdf – Sleep Diary Example
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xQ6xgDI7Whc – Music to help you sleep!
http://www.sleepeducation.org/find-a-facility – Find your closest Sleep Facility
714 N. Senate Avenue
Suite 110
Indianapolis, IN, 46202
Phone: (317) 962-5710
Butler Health Services
HRC, Room 110
530 W. 49th St.
Indianapolis, IN 46208
Main Phone: 317-940-9385
References
https://sleepfoundation.org/sleep-topics/teens-and-sleep
http://www.aasmnet.org/articles.aspx?id=659
http://campusmindworks.org/students/self_care/sleep.asp
https://www.uhs.uga.edu/sleep/
http://www.helpguide.org/articles/sleep/sleep-disorders-and-sleeping-problems.htm
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3eLfn7Ewx_s – video
Healthy Lifestyles in Underdeveloped Countries
November 15, 2015
Within our every day lives the thought of where our next meal is going to come from is not an issue that we have to worry about. In underdeveloped countries however, this is a factor that controls the lives of millions. Poor nutrition, lack of quality education, and severe poverty run the lives of these people. About 2.5 billion people live in underdeveloped countries. Africa and Asia have the most underdeveloped countries, with Latin America contributing as well. Out of the 10 most underdeveloped countries in the world, 8 of them come from Africa, with the remaining 2 from Asia. It is not a shocking fact that the people who are living in these countries do not live healthy lifestyles. This, however, can be a trend that can begin to change. With the right help from organizations and gaining proper education, underdeveloped countries can start to lead more healthy lifestyles.
Hunger
- 795 million people in the world do not have enough food to lead a healthy active life. That’s about one in nine people on earth. The vast majority of the world’s hungry people live in underdeveloped countries.
- Poor nutrition causes 45% of deaths in children under five. That’s about 3.1 million children each year.
- One out of six children (about 100 million) in developing countries is underweight. Within those developing countries one in three children are stunted.
- Under-nourishment is used to describe the status of people whose food intake does not include enough calories to meet minimum physiological needs for an active life.
- Malnutrition is characterized by inadequate intake of protein, energy and micronutrients and by frequent infections and diseases. Starved of the right nutrition, people will die from common infections like measles or diarrhea. Malnutrition is measured not by how much food is eaten but by physical measurements of the body – weight or height – and age. Characteristics include being dangerously thin, being too short for one’s age and being deficient in vitamins and minerals
- Wasting is an indicator of acute malnutrition that reflects a recent and severe process that has led to substantial weight loss. This is usually the result of starvation and/or disease.
Poverty
- Over 2.5 billion people live on less than $2 a day, with nearly three-quarters of the population of Sub-Saharan Africa falling into this category.
- About 1.1 billion people in developing countries have poor access to water.
- About 2.6 billion people in developing countries lack basic sanitation.
- There are about 9 billion children from the developing world. One in three have inadequate shelter, one in five have no access to safe water, and one in seven have no access to health services.
Education
- One in four young people in developing countries are unable to read a sentence
- 175 million young people lack even basic literacy skills.
- An estimated 250 million children are not learning basic reading and math skills, even though half of them have spent at least four years in school.
- 774 million illiterate adults
- There is an increase in teacher numbers because people are being hired without training.
What the Underdeveloped Population Wants
In a study conducted where civilians from 13 different underdeveloped countries were asked the question “What do you want to see change?”, these were the top results:
- Reducing poverty
- Reducing hunger
- Reducing the spread of HIV/AIDS
- Providing more jobs for the youth
- Reducing the death rate of children under five
- Reducing the number of women dying in childbirth
- Achieving primary education for all

What can be Done?
As an individual so far removed from these issues it is difficult to understand how you can help the problem. There are so many organizations trying to combat the issues at hand. Some of these organizations are truly making an impact, while others are sometimes causing even more harm. Many people believe that the issue of world hunger can be resolved if the rest of the world simply donates mass amounts of food to the countries that need it the most. These countries are not accustomed to this surplus of food, and therefore do not understand the proper way to cook and eat the food. This goes back to the lack of education within underdeveloped nations. Without education these problems will not get solved. Children need to be learning from qualified teachers and need to be learning about the importance of health from a young age. This way even if they do grow up in poverty, they know the importance of nutrition and have the knowledge of what foods they can grow for themselves. Physical activity is another aspect that often times gets overlooked. Physical activity is essential in living a healthy lifestyle which is a fact that many people do not understand. If children are learning methods of physical activity in school, and the positive affects it has on the body, they are giving themselves a better shot at living a healthy life.
Resources
- The William and Flora Hewlett Foundation
- Global Partnership for Education
References
- http://www.wfp.org/
- http://www.givewell.org/international/technical/additional/Standard-of-Living#Incomeandassets
- http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/jan/29/illiteracy-education-young-people-developing-countries
- http://www.globalissues.org/article/26/poverty-facts-and-stats
Media References
- https://www.ted.com/talks/josette_sheeran_ending_hunger_now
- http://love2others.org/projects/water/
- http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/delhi-children-malnourished-child-rights-and-you-breastfed-nutrition/1/352583.html
- http://www.imdb.com/title/tt2625598/
- http://factsanddetails.com/world/cat57/sub380/item2155.html
Why Fads Can Become Bad
November 11, 2015
In a society where we constantly strive for perfection, satisfaction or success we often see these characteristics become aspects of everyday life of people. We see this come into affect largely when viewing body image, often we see models, and celebrities photo shopped/altered through media in these unrealistic ways and want to make our bodies look like theirs even if takes drastic measures. Some people have the financial stability to surgically alter their body, while most turn to the internet to find out what the next best diet is. While in the process it is not uncommon to come across a diet that offers you promising results typically in a short amount of time. So you’re telling me I can loose this much weight, this fast just by following these simple guidelines? Most people see themselves on their way to the perfect body in no time but sadly they are mistaken. More than likely what they have found is a fad diet.
What is a Fad Diet?
A weight loss plan or aid that promises dramatic results
- Typically don’t result in long-term weight loss and they are usually not very healthy. In fact, some of these diets can actually be dangerous to your health
Why are they Popular?
- People are willing to try anything that promises to help them look or feel better
- Many people prefer to try the quick fix rather than making long-term changes
- Also many fad diets work for short amounts of time
How to Recognize a Fad Diet?
- Limit your variety of food choices
- Claim to help you lose more than 1 or 2 pounds per week
- Require you to spend a lot of money on things for the plan to work
- Promise that you can lose weight and keep it off without giving up “fatty” foods or exercising regularly
The Atkins Diet
Dr. Atkins, a well- known cardiologist created the Atkins diet which limits the intake of carbohydrates. The idea behind this diet is to change the type of fuel you are burning so that you can lose more or maintain weight. You must reduce carbohydrates which are turned into sugars so that the body is burning and using fat as fuel and weight is being lost even when more calories are being consumed. It is presumed that in your typical diet calories are reduced but the body is still taking in a high amount of carbohydrates which are turned into sugars so our body will cycle between sugar “highs” and “lows”. During these highs the excess sugar will be stored in the body as fat and during the lows you feel fatigued and experience hungry and cravings.
Risks of Low-Carb Diets
Short term:
-Headache
-Bad breath
-Weakness
-Fatigue
-Constipation or diarrhea
Long term:
-Vitamin or mineral deficiencies
-Bone loss
-Gastrointestinal disturbances
-Increased risk for various chronic diseases
The SlimFast Diet
SlimFast is a weight loss plan that is focused on using meal replacements to help support weight loss and dieting. Most SlimFast plans can easily be related to your basic low-calorie diet, the latest of the ever popular Slim Fast plans is their “3-2-1 Plan”. The “3-2-1 Plan” consist of three snack, two meal replacement shakes or bars, and one actual meal per day. Ideally the meal replacements substitute breakfast and lunch while you eat a healthy 500 calorie meal for dinner. The shakes and meal bars advertised to curb hunger for up to four hours, while some still find that they are hunger after consuming them. Also over time products such as SlimFast can become expensive being that their plans call for multiple servings of their products in one day.
Risks of Liquid Diets
Short Term:
-Gallstone formation
-Nausea
-Fatigue
-Constipation
-Diarrhea
Long Term:
-Damage to the intestinal tract
-Impaired liver or kidney function
-Hypoglycemia
-Vulnerability to communicable diseases
-Gaining fat
The Fit for Life Diet
Harvey and Marilyn Diamond created the Fit for Life Diet which is diet based on food combining. The diet disregards calorie counts and controlling portion size but rather emphasizes the idea of combining the correct food and avoiding the wrong combinations of food to eat. This theory roots from the naturalistic view of Diamond, it is “dead foods” that clog or rot in the body while “living foods” cleanse the body. Some “dead foods” would be meats and starches while some “living foods” would be raw fruits and vegetables. A few rules are that no dairy foods should ever be eaten, only fruit and fruit juice should be eaten from the time one awakes until noon, and carbohydrates and proteins should never be put in the stomach at the same time. As one can see a diet like this has very strict restrictions.
Risks of Food Combining Diets
-Vitamin and mineral deficiencies (Calcium)
-Difficultly getting RDA’s
-Gastrointestinal disturbances

How to Lose Weight Healthily?
- Eat a variety of foods to help get all your daily nutrients
- Do not skip meals, especially breakfast
- Exercise on a regular basis
- Avoid calorie dense foods
- Control portion sizes

If you feel the need to change your lifestyle, rather than trying one these fads consult with a specialist which can be found here on our campus.
Butler University Counseling Services
530 W. 49th Street (HRC, Room 110)
Indianapolis, IN 46208
Phone: (317) 940-9385
References:
Davidson, Tish. “Fit for Life Diet.” Diet.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2015.
Lee, Kathrine. “The Slim-Fast Plan.” EverydayHealth.com. Everyday Health, n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2015.
“Nutrition for Weight Loss: What You Need to Know About Fad Diets.” Nutrition for Weight Loss: What You Need to Know About Fad Diets. FamilyDoctor.org, n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2015.
“Weight Loss.” Low-carb Diet: Can It Help You Lose Weight? MayoClinic.org, n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2015.
“Weight Loss Programs & Benefits | Atkins.” Atkins. Atkins.com, n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2015.
Media Sources:
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=fad+diets+commercials
http://bioshieldinc.com/how-can-you-take-advantages-from-raw-food/
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/jennifer-rollin/3-reasons-why-you-shouldn_4_b_8186614.html
Importance of exercise for your average Joe and plain Jane
November 3, 2015
With the new era and advances in technology we have seen the activity rate of the average individual plummet. How does technology relate to our activity levels? Well let me ask you, how often do you drive to work, the grocery store, even to go to the gym to exercise? You are not alone as many individuals fall into the convenience of having that available and so we drive or take public transportation. And the irony is that many individuals drive their vehicles to their local gym to work out and run. The average person needs about 150 minutes a week of activity to stay “healthy” (I put that in quotes because that is an arbitrary term used to label a norm when in reality the health of an individual is subject to their own personal bodies and functions). But exercise does not need to come solely, if any, from a gym or fitness center.
Physical Activity Vs. Exercise
All exercise if physical activity but not all physical activity is exercise. Exercise is a planned schedule to perform a kind of physical activity. Things such as walking for 30 min. However walking to your car is a physical activity and not an exercise. When talking about getting 30 minutes of activity a day for 5 days a week, that includes both physical activity and exercise. Instead of driving everywhere next time think about walking or riding your bike there as these simple changes can help you regulate your activity levels. Or take the stairs next time instead of the elevator.
Increased Physical activity
Weight control- helps prevent weight gain and aids in weight loss by burning calories.
Prevents health conditions and diseases- lowers the risk to many heart related diseases and diabetes.
Improves mood- stimulates brain and leaves you feeling more relaxed and feeling happier.
Boosts Energy- No more being winded or tired throughout the day. Physical activity delivers oxygen that helps you systems work better and more efficient leaving you more alert.
Better Sleep- helps you fall asleep faster and deepens the sleep for an overall better quality sleep
Health benefits
• up to a 35% lower risk of coronary heart disease and stroke
• up to a 50% lower risk of type 2 diabetes
• up to a 50% lower risk of colon cancer
• up to a 20% lower risk of breast cancer
• a 30% lower risk of early death
• up to an 83% lower risk of osteoarthritis
• up to a 68% lower risk of hip fracture
• a 30% lower risk of falls (among older adults)
• up to a 30% lower risk of depression
• up to a 30% lower risk of dementia
It can reduce your risk of major illnesses, such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and cancer by up to 50% and lower your risk of early death by up to 30%
Not all activities or exercises are created equal
Whether you go to the local gym or increase your daily activity levels in your life the activities only count towards benefiting health if you are moving quick enough to raise your heart rate, breathe faster, and feel warmer. Just because you are taking the stairs now instead of the elevator it does not mean you walk up the stairs at a slow pace. The main objective is to get your body moving and to get your breathing harder and faster. One way to test if the activity is increasing heart rate and breathing rate is by doing a talk test. A talk test is a self evaluation while exercising that shows if you are able to talk but cannot sing a song. If you are unable to sing a song then that activity is working.
Moderation
The biggest word you will hear in this post is moderation. This blog is not written to make you drastically change you ways and have you out and exercising everyday and eating the right foods and getting the proper amount of sleep. It is to keep you aware of your body and possible threats that could occur with lack of physical activity. It is here to help you reflect on your daily routine and to make changes where you deem necessary. Maybe instead of watching television for 2 hours, you watch for 1 hour while doing sit ups or moving around. The main objective is to stray aware from a sedentary life and gradually move into a more active lifestyle which will have numerous benefits on your health.
Resouces:
Talk to your doctor before starting a new regimen
Access to Health 12th edition
Works Cited:
Donatelle, R. J. (2012). Access to Health (12th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Pearson Benjamin Cummings. Donatelle, R. J. (2012). Access to Health (12th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Benefits of exercise. (n.d.). Retrieved November 3, 2015.
Fitness. (n.d.). Retrieved November 3, 2015.
Images:
http://cache4.asset-cache.net/gc/467180649-new-jersey-jersey-city-happy-man-on-weight-gettyimages.jpg?v=1&c=IWSAsset&k=2&d=PHreAxwUsT8X7jaWqvQENC9WtMKprHo6wW3FAN%2FKm4lKORPhscQtlrpl6Tsae9Ml
http://innovahealth2012.info/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/koko.jpg
http://livehealthy.chron.com/DM-Resize/photos.demandstudios.com/getty/article/41/134/78468149.jpg?w=650&h=406&keep_ratio=1&webp=1
Videos:
The Need for Creatine??
November 2, 2015
What is it and how can it be used?
“Creatine is a chemical that is normally found in the body, mostly in muscles. It is made by the body and can also be obtained from certain foods. Creatine is most commonly used for improving exercise performance and increasing muscle mass in athletes and older adults. There is some science supporting the use of creatine in improving the athletic performance of young, healthy people during brief high-intensity activity such as sprinting.”
Do you need it?
Who you are and what your goals in life are can give you that answer. Whether you are an athlete, a gymrat, or an average individual, creatine will always be found within the human body. With those individuals, fitness level, age, sport, and the dose can effect how the body reacts and ultimately puts the added creatine to work. The reason people use creatine is to simply supply the body with needed energy to make muscles perform at their best.
We do however receive creatine through our diets. The best way to receive creatine through eating would be to consume poultry, meat, and fish.
What will it do for the body?
Good
- Increase the amount of energy available to working muscles*
- Creates ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)*
- Increase muscle mass*
- Pulls water to muscles**
- Less fatigue*
- Faster muscle recovery*
- Weight gain*
Bad
- Nausea*
- Cramping*
- Dehydration*
- Increased blood pressure*
- Weight gain*
- Pulls water to the muscles**
* Not the same for every individual!
**Hydration is key when taking creatine
Popular Facts & Myths
Creatine is the same as anabolic steroids? Myth, steroids mimic testosterone whereas creatine is naturally produced.
Creatine causes weight gain? Fact, creatine pulls water to the muscles and it is the main point in taking the supplement (you gain muscle fibers when you start to workout).
You shouldn’t take too much? Fact, no more than 20 grams a week is needed, any more is illogical.
Resources: Contact you doctor/local nutritionist to see if creatine is right for you.
References:
“Creatine Facts and Myths.” Men’s Health. Web. 3 Nov. 2015
“Pros and Cons of Creatine-HRFnd.” HRFnd. 15 Mar. 2014. Web. 3 Nov. 2015.
Annussek, Greg;, “creatine.” A Dictionary of Nursing. 2008, “creatine.” A Dictionary of Biology. 2004, and David A. “Creatine.” Encyclopedia.com. HighBeam Research, 2005. Web. 3 Nov. 2015.
“Creatine: MedlinePlus Supplements.” U.S National Library of Medicine. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Web. 3 Nov. 2015.
Images:
http://store.bbcomcdn.com/images/store/prodimage/prod_prod2060042/image_prodprod2060042_largeImage_X_450_white.jpg
https://images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com/images/G/01/aplus/detail-page/B001G8Y8U8_creatine_hp_sm.jpg
https://www.fourbody.com.au/images/P/Musashi-Growling-Dog-Creatine-500g_8.jpg
http://piacomm.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Water-bottle.jpg
The Ninety Percent
October 26, 2015
A New Science
Sports and Exercise Psychology was born in Germany during the 1920’s. It has since developed into a complex interdisciplinary science reaching far beyond just one blog post. One of the most popular applications of this science is at the elite level of sports competition. Athletes looking to gain a competitive edge or take their training to the next level turn to sports psych. methods ranging from quick tricks to mental strength sessions with qualified professionals. Here are some of the mental skills that have emerged from this growing field of study designed to develop the mind of a champion…

Goal Setting
- Specific
- But within a range:
- Rather than focus on one end-all-be-all goal, have a range within you wish to fall.
- Making successful performance life or death means dying an awful lot.
- But within a range:
- Measurable
- There must be a point where the goal is clearly achieved
- Objectivity means there is a definite point of success
- Positive
- Focus should be on high achievement
- Focus should not be on simply not failing
- Inspiring
- Short term and long term goals keep maintain motivation
- More ambitious goals are easier achieved with many small goals
- Aim High
- Displayed
- Think it, then Ink it
- Your mind should be drawn toward your goal throughout the day
- Placing reminders on the bathroom mirror, setting an alarm at a significant time, pictures and symbols are helpful reminders.
Visualization
Jim Afremow’s book, The Champion’s Mind, cites research that suggests the brain can be tricked into believing both reality and vividly imaged experiences.
Example: A nightmare where an individual is being chased elicits the same response as a real fleeing experience. When the dreamer wakes up he is safely at home, yet frightened, breathing fast, and heart pounding adrenaline throughout his body.
This is why visualization can be used to put an athlete in a competitive situation, prepare him or her for the situation, and yet never leave his or her own home. An athlete who practices visualizing a situation finally reaches that point in competition and can flow rather than strain. The scenario is familiar; along with the stress, anxiety, discomfort, and the solution. A study recently published in the Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology found biological evidence of some individuals having better visualization abilities than others, but that through practice, an athlete can increase his or her visualization skill. Jim Afremow offers his “three key ingredients for successful imagery rehearsal”:
- Vividly see yourself performing successfully
First-person point of view, as opposed to third-person, allows the situation to become your own. Seeing yourself in a stressful situation is less effective than feeling yourself in a stressful situation.
- Deeply feel yourself performing masterfully
In your visualization, you can only perform as well as you imagine yourself performing. Visualizing that you have mastered the situation will help you to master the real thing.
- Thoroughly enjoy seeing and feeling yourself winning
After addressing that the scenario is stressful, one coping mechanism is to make the stress as enjoyable as possible. The more positive thoughts going through your head, the better you will be able to perform.
+Self-Talk

The “Good Wolf” for our purpose is also the animal of flowing, smooth, effortless performance. Practicing positive self-talk can sound silly at first. In the beginning, you may feel as though you are lying to yourself, that this is another way to “fake it ’til you make it.” However, as with visualization, your body can be tricked into a better state of mind. With practice positive self-talk becomes a positive attitude.
“Do Say Do!”
This was a phrase coined by cross country Coach Kyle Burton. He suggested that athletes should not allow negative thoughts to enter their minds. This does not mean avoiding adversity entirely, but keeping a positive attitude when things do not go your way. Rather than tell yourself, “Don’t fall off this pack.” A runner should tell himself, “Stay in contact with this group.” Practicing telling yourself positive affirmations forces the bad thoughts out and the good thoughts in. The good wolf thrives in competition.
Confidence
“When I race, my mind is full of doubts-whol will finish second, who will finish third?”-Noureddine Morceli
Confidence is mistaken for a multitude of other attitudes: cockiness, no fear of failure, pride, arrogance. A true champion builds genuine confidence. Clarity breeds confidence; not the other way around. This is where we begin to see false senses of confidence. Building clarity means you must be very familiar with your flaws and failures, and you must be self-actualized with your successes. This means you should not fear failure. Failure is a very real measure of where you are at, and what you have to build upon.
Body Language
Below is a TED Talk video blending together many of the mental skills discussed above. This particular talk emphasizes the power of positive body language over mentality. Follow along with some of the tips and tricks in the video.
Related Readings:
- Biological Evidence of Imagery Abilities
- Patterns of Change in Psychological Variables Leading up to Competition
- The Champion’s Mind: How Great Athletes Think, Train, and Thrive -Jim Afremow
- The Energy Bus -Jon Gordon
- Running Within -Jerry Lynch
Helpful Resources:
- Journal of Sports and Exercise Psychology
- http://journals.humankinetics.com.ezproxy.butler.edu/jsep
- Coach Ken Wertz Mental Magic
- Twitter: @MentalMagicII
- St. Vincent’s Sports Psychology
Works Cited
Boat, R., & Taylor, I. M. (2015). Patterns of Change in Psychological Variables Leading up to Competition in Superior Versus Inferior Performers. Journal of Sports & Exercise Psychology, 244-256.
Cuddy, A. (2012, June). Your body language shapes who you are. Retrieved from TED.com: https://www.ted.com/talks/amy_cuddy_your_body_language_shapes_who_you_are
Seiler, B. D., Monsma, E. V., & Newman-Norlund, R. D. (2015). Biological Evidence of Imagery Ablities: Intraindividual Differences. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psycology, 421-435.
The Wolf Within.
Wikipedia. (2015, October 5). Sports Psychology. Retrieved from Wikipedia.com: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sport_psychology
Which Mood Disorder Is It?
October 20, 2015
What does “Mood” mean?
Everyone faces a period of feeling down, sadness, happiness or sometimes a big all of energy. That is just part of being a human and ordinary life but in this world, a small population of people have these disturbances that are not normal. These disruptions are called mood disorders. When many people think of mood, it is often referred to their feelings. For example, “I am in a happy mood, ” but health professionals look review mood differently. In a clinical setting, it is used as a persistent emotional state that affects how a person sees the world.
College students face many mental health issues that are left untreated and can often drain students and is important for students to take action now. Research by the National Alliance on Mental Illness on college campuses show:
1 in 4 students have a diagnosable illness
40% do not seek help
80% feel overwhelmed by their responsibilities
50% have been so anxious they struggled in school
Depression
Depression is the number one reason why students drop out of college. It is an easy getaway and if it is left untreated, it could lead to other symptoms and suicide. It is said that 36.4% of college students have experienced some level of depression in 2013. Depression is a common illness that interferes with life making it hard to eat, sleep, work and makes you feel helpless. Depressive illnesses are disorders of the brain and are likely caused by a combination of genetics, biological, psychological and environmental factors. Knowing how you handle feelings, stress, heartbreak, an isolation may help you realize when you are depressed.
Symptoms:
-Feelings of sadness or unhappiness
-Change in appetite or weight
-Slowed thinking or speech
-Loss in energy and sleeplessness
-Trouble concentrating
-Thoughts of suicide
Though you may see signs in yourself, you may have a friend whose behavior has been changing recently. Here are recognizable signs of depression of a friend:
-They are no longer engaged in activities they once loved
-They are experiencing extreme anger or sadness over a relationship in their life
-They are talking about death or suicide
-They no longer attend classes or social outings
Treatment:
-Psychotherapy (talking therapy) used to treat mild and moderate forms of depression
-Antidepressants prescribed by family doctor
-Electroconvulsive therapy: release of chemicals in the brain that aid communication between nerves
S.A.D. Syndrome (Seasonal Affective Disorder)

SAD syndrome is a mood disorder that is associated with depression and seasonal variances of light. It affects half a million of people in the winter season between the months of September to April. The symptoms soon calm down during the spring and summer months but still have different affects. Majority of in people deal with SAD syndrome from age 18 to 30. It is more typical for women to suffer from it; 3 out of 4 SAD sufferers are women. It also affects more or less to people depending on their geographical location.
Symptoms in winter months:
-Tiredness
-Low energy
-Weight gain, cravings for foods high in carbohydrates
-Oversleeping
Symptoms in summer months:
-Depression
-Trouble sleeping
-Weight loss
-Poor Appetite
-Anxiety
What causes SAD Syndrome?
As seasons change, different sunlight patterns cause a shift in the circadian rhythm and causes these biological clocks to become irregular with daily schedules. The hormone melatonin, a sleep-related hormone secreted in the brain, has been linked to depression because the mormons has increased levels in the dark. So when there is shorter days and longer nights, the secretion of melatonin increases.
Treatment:
For mild symptoms, spending time outdoors in the sunlight relaxing or doing work is helpful. For severe symptoms, bright light therapy or phototherapy decreases the secretion of melatonin in the brain. If light therapy does not work, it is possible to be prescribed to an antidepressant drug to reduce the symptoms.
Postpartum Depression
Often people may think having a baby is beautiful and brings joys to life. Though that is true for some, other women may face postpartum depression.. Postpartum Depression is a depression after a woman gives birth to her child. It can occur immediately after delivery or up to a year later but most of the time, it occurs within the first three months after delivery. This depression can look like the normal “baby blues” except that postpartum depression symptoms last longer and more severe.
Symptoms:
-Lack of interest in your baby
-Negative feelings towards your baby
-Worrying about hurting your baby
-Lack of concern for yourself
-Feelings of worthlessness and guilt
-Changes in appetite or weight
-Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide
Causes:
The three most common causes are hormonal changes, physical changes, and stress.
Hormonal changes: Women experience a huge drop in estrogen and progesterone hormone levels and huge drop in thyroid levels. These hormonal changes may trigger postpartum depression.
Physical Changes: Women could be dealing with pain form difficulty or struggle with the weight gain and trying lose it leaving women insecure about themselves.
Stress: Women are often overwhelmed and anxious about the ability of taking care of their baby. This can be difficult to adjust to and cause stress.
Coping and Treatment:
The best way to cope with the depression is to take care of yourself for physical and mental well being. Here are some tips and lifestyle changes:
-Don’t skip on sleep
-Set aside quality time for yourself
-Make meals a priority
-Get out in the sunshine
-Ease back into exercise
If self-help did not work, there is always professional treatment
-Antidepressants
-Hormone Therapy
-Individual Therapy
Resources:
Counseling and Consultation Services (HRC, 120)
Anxiety and Depression Association of America
Society for Light Treatment and Biological Rhythm
http://www.websciences.org/sltbr
References
“Mood Disorders.” Mood Disorders. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
“Top 5 Mental Health Challenges Facing College Students.” Best Colleges. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
“Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).” Mental Health America. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
“Postpartum Depression and the Baby Blues.” : Symptoms, Treatment, and Support for New Mothers. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
Media Sources:
https://www.etsy.com/market/think_happy_thoughts
http://www.babycenter.com/0_postpartum-depression-and-anxiety_227.bc
http://kidshealth.org/teen/your_mind/mental_health/sad.html
Crash Course to Anxiety Disorders
October 19, 2015
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a mental state that is characterized by persistent and chronic feelings of threat or worry. It usually occurs when some aspect of your life feels uncontrollable or temporary feelings of stress are not relieved. Anxiety symptoms can be alleviated quickly if taken care of, or they can manifest into an anxiety disorder. An anxiety disorder occurs when symptoms of anxiety affect a person’s ability to function in daily life. You can determine if you have an anxiety disorder by visiting your doctor and having them evaluate your medical and mental health history, performing a physical exam, and usually a drug test because some medications and drugs can have side effects that are similar to anxiety symptoms.

Being aware of anxiety disorders is important because, as college students, we are in a time of our lives that is high-risk for developing an anxiety disorder. According to our textbook, Access to Health, 40 million Americans over the age of 18 suffer from some type of anxiety disorder. This is shown even more by the statistic that 9.4% of undergraduates deal with anxiety. That may not seem like much, but anxiety is something that no one should have to deal with, especially college students with so much on our plates. The presence of an anxiety disorder is more often than not accompanied by depression as well. Depression can lead to a whole other set of problems outside those associated with anxiety disorders. Both anxiety and depression lead to self-harm behaviors, which 17-38% of college students with anxiety disorders do.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
This disorder is characterized by chronic symptoms of anxiety with no particular trigger that the person can pinpoint. To be diagnosed with GAD, you must have at least three symptoms for more days than not over the period of six months. Symptoms of anxiety include irritability, inability to concentrate, muscle tension, restlessness, being easily fatigued, and unrealistic and exaggerated worry about every day events. There are no concrete causes of any anxiety disorder, but GAD seems to run in families.
Panic disorders are characterized by the occurrence of panic attacks. Panic attacks are short-lived, intense physical reactions to anxiety. They can last up to a half hour, depending on the severity. These attacks involve physical symptom such as an increased rate of breathing, hot flashes, stomach cramps, chest pain, chills, having trouble swallowing, and a feeling of being doomed or sense of death. Some professionals think this could be an over reactive fight or flight response. They leave the person feeling drained and very tired. Panic disorders can make people very anxious about going out in public places because of the occurrence of panic attacks, which becomes destructive to their life. Panic disorders increase the likelihood of developing agoraphobia, which is the fear of being in any place or situation that is hard to escape from in the event of a panic attack. Panic attacks can be triggered by a source of anxiety that the person deals with, or could happen for no reason. According to Access to Health, 6 million Americans over the age of 18 suffer from panic disorders. They usually show up in early adulthood and are more common in women than in men.
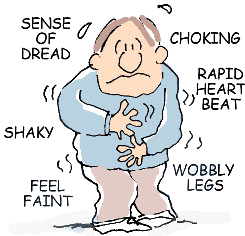
Phobic Disorders
Having a phobia means that you have an irrational and persistent fear of something specific, like an object, activity, or situation. With this irrational fear comes the intense need to avoid that particular trigger of fear/anxiety. Common phobias include arachnophobia, fear of spiders, and social phobia, fear of being humiliated or embarrassed in social situations. Social phobia tends to lead to people avoiding social situations altogether.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is characterized by repetitive behaviors such as rituals, and recurrent, unwelcome thoughts. A lot of times people with this disorder have an intense fear of germs or of dirtiness, and want things to be exactly symmetrical and in order. The difference between OCD and other anxiety disorders is that the people who have it know that their fear and behaviors are irrational but do not have the power to stop it. All of us have a little bit of OCD about certain things, but to be diagnosed with the actual disorder it has to interfere with your daily life and OCD behaviors take an hour or more of your time per day. OCD usually starts to show up in adolescence or early adulthood, around the age of 19.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
People develop PTSD after witness or experiencing a traumatic event, such as terrorism, an accident, assault, a natural disaster, or war. Access to Health again provides a statistic: 1 in 8 cases of PTSD are soldiers. Of the people who have PTSD, less than half of them receive professional help for it. Symptoms of PTSD include insomnia, flashbacks, nightmares, acute anxiety, dissociation, and possibly nausea when they recollect the event.
Possible Causes of Anxiety Disorders
No one really knows what exactly causes someone to develop an anxiety disorder, but there are some factors that tend to contribute to them. The biology of someone’s brain and the way it functions may make them more susceptible to developing an anxiety disorder. Doctors and psychologists have used PET scans to analyze how the brain reacts to certain events in people with an anxiety disorder. Going along with brain biology, heredity seems to play a role in anxiety disorders as well.
Other factors that may contribute to anxiety disorders are environment and social/cultural roles. Your environment and the way you respond to it could program your brain to respond in a certain way every time that particular thing happens in your environment. The way your parents respond to things can also make an impression on the way you respond to the same thing. Social and cultural roles differ between men and women. It may seem like more women deal with anxiety disorders but it could be that men repress their anxiety because of the way it would look to the rest of society. In society it is more acceptable for women to express their anxiety because people may almost expect it from women.
Treatment
There are multiple ways to go about getting help for an anxiety disorder, but not every method is right for every person or disorder. It is important to seek professional help if you feel that anxiety is interfering with your daily life and ability to function. The professional can help you from there and give recommendations for what may work for you. Treatment for anxiety disorders include therapy sessions, certain medications, and coping strategies.
You might say…so is there a difference between anxiety and stress? Watch the video for more info: 
If you feel like you may have an anxiety disorder or know someone who might, don’t hesitate to take care of it! You can seek help at a resource right on campus:
Butler University Counseling Services
530 W. 49th Street (HRC, Room 120)
Indianapolis, IN 46208
Phone: (317) 940-9385
References
Donatelle, R. J. (2012). Access to Health (12th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Chen, J.-P., Reich, L., & Chung, H. (2002). Anxiety disorders. Western Journal of Medicine, 176(4). Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1071743/.
Media Sources:
http://yourliferecoverycenter.com/panic-anxiety-disorder/
http://brainprick.com/how-to-deal-with-anxiety-disorders-and-gain-peace/
http://anxiety-treatments.com/
http://youtube.com/ watch?v=1g_AxF9nLzQ
Type 1 Diabetes: Don’t Sugar Coat It
October 12, 2015
Diabetes affects more than 29 million people in the United States. Depending on the type of diabetes, factors contributing to this disease are related to obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetics. Insulin, a hormone, is used to transport glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of the body and therefore plays a large role in regulating blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in younger patients and is when the body cannot produce enough insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the patient’s body cannot use the insulin it produces. Type 2 diabetes is more often diagnosed in adults, more specifically African American, Latino, Native American, and Pacific Islander individuals.
What factors can lead to T1D?
Diagnosis of type 1 diabetes can often result from a genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Often those with type 1 diabetes inherent risk factors from both parents, not just one. Type 1 diabetes develops more commonly in winter and is more prevalent in areas with colder temperature. Viruses also affect the onset of type 1 diabetes. A virus that may have a mild effect on one individual, may onset type 1 diabetes in another individual who is predisposed to the disease. Additionally early diets play a role in developing diabetes as T1D is less common in those who were breast fed than those who were not.
Blood Glucose Testing
How and when to test:
- Insert a test strip into the meter.
- Use the lancing device to get a drop of blood from the fingertip.
- Touch the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result.
- Your blood glucose level will appear on the meter.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Medication: Those with type 1 diabetes are unable to produce sufficient insulin from their pancreas. Therefore blood glucose levels must be monitored and controlled through daily injections of insulin through an insulin pen, syringe, or pump.
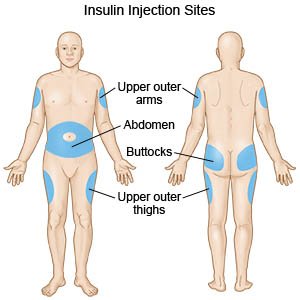
Exercise:
Exercise is a powerful tool to balance insulin doses. Responses to exercise on blood glucose levels before starting activity, intensity and duration of the activity, and recent changes in insulin doses. Often individuals with T1D experience a drop in blood glucose levels. If blood glucose levels drop to a certain level, hypoglycemia will occur. In this situation it is important to carry a carbohydrate food or drink that will quickly raise levels.
Blood glucose can also run high during or after high intensity exercises that increase stress hormones. If blood glucose levels are high before exercise, it is important to check for ketones in the blood or urine. If ketones are present, exercise should not occur.
Technological Advances
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small computerized devices that deliver insulin in steady measured and continuous doses, known as basal insulin, and as a surge dose around meal times. The pump injects insulin through a catheter, a small flexible plastic tube. The catheter is inserted through the skin into fatty tissue. While monitoring of blood glucose levels is still needed, insulin pumps allow those with T1D to better control their glucose levels. The delivery system mimics the pancreas’s normal insulin release responses.
Advantages:
- Replaces individual insulin injections.
- More accurate delivery of insulin.
- Results in fewer swings in blood glucose levels
Disadvantages:
- Can cause weight gain.
- Can cause diabetic ketoacidosis if catheter comes out on accident.
- Can be expensive.

Dexcom Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Dexcom offers a variety of blood glucose monitoring products such as the Dexcom G5, which allows dynamic glucose pattern monitoring. Dexcom created an implantable sensor that the body would not reject and that would perform for an extended period of time. The Dexcom reveals if glucose levels are trending up, down, or if it is at the appropriate level. The Dexcom CGM also has Bluetooth settings that allows the readings to be shared with loved ones across the country.
My Amazing Grace
On December 26, 2015 my little cousin Grace went into Ketoacidosis- her blood glucose levels were over 400 mg/dl. After being rushed to the hospital Grace was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at age 8. Since her diagnosis, Grace has proved to be the strongest, most courageous little girl. She currently uses a Dexcom G4 to help monitor her blood glucose levels. She will be able to explore the insulin pump as an option this upcoming December. She looks at her diagnosis as just part of everyday life and does not let it slow her down. She has a passion to spread awareness about T1D.

Resources:
http://www.diabetes.org/
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/science/science-news/11151909/Cure-for-Type-1-diabetes-imminent-after-Harvard-stem-cell-breakthrough.html
References:
http://www.diffen.com/difference/Type_1_Diabetes_vs_Type_2_Diabetes
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/blood-sugar/ART-20046628?
http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticles.nsf/pages/Diabetes_-_long-term_effects
Food Deserts: How Far Are You From A Fresh Apple?
October 5, 2015
A Looks at the Realities of the Underprivileged
In every corner of the country a frightening trend has been happening in our poor rural and urban areas, food deserts leave families without access to nutritional foods and every day necessities, and the results are already affecting every one of us. Food deserts are defined by the USDA ‘urban neighborhoods and rural towns without ready access to fresh, healthy, and affordable food.’ More specifically the residents have to live anywhere from 2-6 miles from a true grocer in urban areas, and the majority of people living in the area must live below the federal poverty level and have limited means of transportation, private or public, in order for it to be classified a food desert. Today there are over 23.5 million people in America that are currently living in a food desert, a large amount of them families, and that number is growing rapidly.

While this tragedy effects quite literally millions of families, it is seldom talked about, and the majority of America has no idea what in the world a food desert even is. In this blog post we will discuss some reasons for food deserts, results of food deserts, who food deserts affect, and new and innovative ways communities are rising up to help one another and end this crisis.
Indianapolis is the Worst City in the Country for Food Deserts
A not so fun fact for residents of the largest city in the state of Indiana, Indianapolis ranks dead last in the country for the amount and severity of food deserts found within its’ city proper. As a matter of fact nearly 50% of the east side of Indianapolis is classified by the USDA as a food desert, as shown in the graphic below. To add on the that are some disturbing statistics unique to the food deserts of Indianapolis, 40% or more of the residents make 200% or less of the federal poverty minimum, meaning they make less than half of the federal poverty level. As is expected at that income level, those families typically do not own vehicles, leaving them to either walk, bike, or rely on Indy’s notoriously spotty public transportation to get to and from the nearest full grocery store, making an hour long chore for most people a multiple hour long endeavor for people who are just trying to supply their family with fresh foods and vegetables. With the closing in 2014 of the four Double 8 Food locations around the poorest areas of Indy, residents found it almost impossible to find an affordable source of nutritional foods within multiple miles, and many of these residents, including a significant amount of senior citizens, are feeling hopeless and without option as their only source for food becomes fast food franchises and the junk food that is available at the gas station.

So What?
The simple reality is that if you live in a suburb, or even in a typical urban neighborhood, you don’t live in a food desert, or maybe not even close to one, and that may make it hard for you to connect to this sad truth. It is hard to understand the severity of this when you are not living it, and that is perfectly fair of someone. Most of us spend our lives with the assumption that when you want to get quality meat, vegetables, whole grains, or fruits you (or your parents) drive to the grocery store and stock up for the week, that’s that, the fridge is stocked for some time to come. Fair enough, but what happens when you don’t have a car, and that grocery store that’s ‘just around the corner’ is in reality a mile and a half away, and there isn’t a bus route by you so you’re only choice is to walk to the store, get a weeks worth of food for you and your family, then walk a mile and a half back with 30 pounds of groceries? You might think it is definitely a burden, but it’s a mile and a half, you walk further than that with a backpack every day! Right, now imagine doing that once or twice a week, after working a full time job, for years on end, through the 100 degree weather in Summer, and even worse the 0 degree weather in Winter. The thing is, you’re lucky in these neighborhoods if your family can even do that, most families don’t have the time to do that, so the only option now is fast food or whatever you can find at the gas station or corner store. Well when that is the majority of your diet you will obviously have an increased rate of obesity and all of the health problems that come with it, diabetes, heart attacks, higher rates of cancer, and so on. When a significant portion of the population has higher rates of health problems, we as a society all pay for it when they make their trips to healthcare facilities, add on to the matter that if the are below the poverty level the chances of them having insurance are near 0, so their healthcare costs largely get passed on to the tax payer. So I can assure you, even if this is a problem you have never heard of or don’t even really care about, it is certainly affecting you and will continue to do so for decades to come.
Well, What Can I Do?
The natural question following all of this information is ‘okay, well now what?’ How can you as an individual create any meaningful change to combat this problem? It’s a tough question to answer, as there is no one way, each community is different and requires a different solution, some more severe than others. The very first thing you can do is educate yourself further on the matter, at the bottom of this post I have multiple resources you can access to gain a better picture of the food desert crisis in America that are all free to access and go further in the issue. After that I suggest learning of the food deserts specific to your area, be that urban or rural, and learn about their specific causes and problems; the solution for a food desert on the east side of Indy will likely not be the same as that of a small town in rural Indiana 100 miles north. From there, it is totally your decision, write to your local politician or congressmen to try and call attention to the issue, get it known on social media, recruit others in the community to call awareness to it, these are all things you can do from the comfort of your own house. If you are more of a hands on individual I would recommend this video:
The single biggest thing communities are getting together and doing to fight food deserts is urban gardening, as it is cheap, practical, economic, and green. Getting a small group of people together, and taking a small plot of land in a public area or a private/abandoned lot (with permission) and planting rows of edible vegetables and fruits has become a trend that’s sweeping the nation. You do not need much space to build raised beds to grow tomatoes, cucumbers, squash, lettuce, etc. in, you can do it in a park, an alley, on a rooftop, on the side of a building even. Urban gardening is the single most prevalent solution to dealing with food deserts, and it makes sense why. The costs are negligible, and you are allowing fresh and nutritious foods directly into the hands of community members at low or no cost, the only serious investment from you is time.
With all that said, how you choose to end your local food desert is 100% up to you and the people you organize with, there is no one size fits all solution, but getting out there and making attempts to better the community will always be more beneficial than letting it sit there and sink further.
For More Information:
- http://indyfoodcouncil.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Indianapolis-Food-Related-Initiatives-Assessment-A-SPEA-Capstone-Project.pdf
- http://indianapublicmedia.org/news/indianapolis-ranks-worst-nation-food-deserts-67800/
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=jicYbi-8ZNU
Stress What’s That!?
September 29, 2015
A Quick Guide to Managing Stress in College
Everyone has stress, whether its good stress or bad stress, your body takes a toll. Your body does not know the difference so learning to manage stress is important. College is a time of life changes and environmental differences, which means there is a high level of stress. Stress can be anything from a big test, to going on a date! Before I go into the different ways to manage your stress, lets name some of the top general topics that cause high stress.
- Money
- Work
- Health
- Family
- School
Everyone has been stressed about one thing or another on that small list. College is a time where all of those things attack you. School is expensive, you are away from you family, college is hard work, and have you ever heard of the freshman 15? Learning how to manage these things in your life can help you from getting sick, and causing more pain than your body really needs.
Many people don’t think they can manage stress. Things just keep pilling up and it never seems to stop. However, you have full control of what goes on in your life and how to handle every situation. Every person has a different personality and body; there is more than one way to deal with stress. However, if nothing is done about it then a certain stress management strategy is probably necessary. It is important to learn different remedies and find a fit that is best for you. Before you can find the best way to cope with stress, you need to understand where your stress is coming from and why you are getting stressed. So before you decide to manage your stress ask yourself these questions
- Is the stress temporary? (I just have a lot of stuff going on right now)
- What is my main source of stress? (family, school)
- Do you blame yourself or others for your stress?
Okay now once you have these questions answered you can figure out the best way to deal with your stress. You can take some simple everyday remedies, or if you think you need more, follow some of the more step-by-step tasks.

REMEMBER TO BREATHE
FIRST I want you to take three deep breaths (Yes right now, even if you’re not stressed). Don’t you feel better already? You may think this sounds dumb, but people often forget to breath in stressful situations. Deep breathing is scientifically proven to affect the heart, brain, digestion and the immune system. When we get really stressed, or mad there is a phrase termed ‘my blood is boiling’. Well your blood is not actually boiling, but you blood pressure increases and the pH is rising. Doing these deep breathing exercise can actually have the ability to alter these factors. So next time you need a study break, stop and do some yoga, or before you call your mom back after she left you a long voice mail, practice some breathing techniques.
If you are interested in specifically breathing techniques, check out these websites!
- http://healthland.time.com/2012/10/08/6-breathing-exercises-to-relax-in-10-minutes-or-less/
- http://www.webmd.com/balance/stress-management/tc/stress-management-breathing-exercises-topic-overview
PEP TALKS
Now that you are done breathing, lets give our selves a POSITIVE SELF PEP TALK. Yes, you read that right. Tell yourself how awesome you are and how great you are doing. Everyone needs positive reinforcement in his or her life, and what individual knows you better than you! When ever you are at your desk, or in your car tell yourself “you can do it” or “things could be worse.” I challenge you to give yourself one encouraging word or phrase a day. Here are some examples to help you:
- “I’ve got this”
- “This is going to be easy”
- “I can handle this”
- “I can always ask for help”
- “I will look back at this and laugh”
- “I will get through this”
GET UP AND MOVE
Another everyday task people forget about is movement and exercise. Having daily activity can be a huge stress reliever. Exercise releases endorphins and helps your body to feel good. You don’t have to be a heavy weight lifter to make this happen; any movement will help keep your mind off your worries. Taking as little as 10 minutes to get your heart rate up can help you step away from your worries and sweat out some stress. A regular workout routine can be very beneficial but doing little things like walking your dog, using the stairs, or even putting on some music and dancing is beneficial. The longer you sit around the longer your stress will sit on you.
WRITE IT DOWN!
If you love to write and journal, then this technique may be suitable for you. Not only writing down your feelings, and situations that are stressful can help, but also going back and preventing them from happening again is even better. Keeping a stress journal can help you find the regular stress influences in your life. In this journal keep track of:
- What caused your stress
- Where you were
- How you felt both mentally and physically
- What your reaction was
- How you relieved the stress
After the stress is relieved, you can go back and look at the different entries and analyze what was the same or different. Here you can figure out what small changes need to be done in everyday life to keep the stress from coming back. You may not have noticed the pattern before so this can keep you organized and accountable. Looking back at these situations you can decide what was unnecessary stress you need to take care of in your life, or how your reaction may affect others. Some situations may not be things you can change, but this can be an opportunity to accept that. We can’t change that the sky is blue, and if I am always worrying about why the sky is blue and not purple what is the point? I can accept the things I cant change and move on from it.
Again these are only some of the way to deal with stress, but they are easy to forget. Here are some other quick options for relieving stress:
- Smile and laugh
- Seek out friends
- Eat healthier
- Avoid drugs and alcohol
- Time manage
- Pick up a hobby
- Stay positive
- See a counselor

There are different ways individuals cope with stress, but don’t let it get the best of you. When in doubt stop breathe and talk yourself through it. Always remember it could be worse and there is always someone rooting for you.
For more information:
- http://cmhc.utexas.edu/stress.html
- http://healthfinder.gov/HealthTopics/Category/health-conditions-and-diseases/heart-health/manage-stress
- https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001942.htm
- http://www.cdc.gov/features/handlingstress/
- http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/manage-stress.aspx
For counseling services contact:
Director: Keith Mangus
Butler University Counseling Servies
HRC, Room 120
530 W. 49th St.
Indianapolis, IN 46208
(317) 940-9385
http://legacy.butler.edu/counseling-services/
References:
Thompson, Dennis. CBS News. The Biggest Cause of Stress in America Today. 2015. Web. Sept. 2015. Retrieved from: http://www.cbsnews.com/news/the-biggest-cause-of-stress-in-america-today/
Robinson, L. Smith, M. Segal R.Help Guide. Stress Mangement: How to Reduce, Prevent, and Cope with Stress. Web. Sept. 2015. Retrieved from: http://www.helpguide.org/articles/stress/stress-management.htm
Cuda, G. NPR Books. Just Breathe: Body Has a Built-In Stress Reliever. 2010. Web. Sept. 2015. Retrieved from: http://www.npr.org/2010/12/06/131734718/just-breathe-body-has-a-built-in-stress-reliever
American Heart Association. Four Ways to Deal with Stress. 2014. Web. Sept. 2015. Retrieved from: http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/GettingHealthy/StressManagement/FourWaystoDealWithStress/Four-Ways-to-Deal-with-Stress_UCM_307996_Article.jsp
American Psychological Association. Five Tips to Help Manage Stress. Web. Sept. 2015. http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/manage-stress.aspx
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Manging Stress. 2012. Web. Sept. 2015. Retrieved from: http://www.cdc.gov/features/handlingstress/
Media Sources:
https://worldofblackheroes.files.wordpress.com/2011/03/you_rock.gif
http://ctworkingmoms.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/breathe.jpg
http://www.michaelomidi.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Exercise-and-Anxiety.png
http://cpxicom.c.presscdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/no-stress.jpg
http://roughcityathletics.com/2015/03/17/stress-adaptation-cycle/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0fL-pn80s
Can Stress actually Kill you?
September 29, 2015
What is stress?
In our world as college students “stressed” has become a way of life. “How are you today?” “So stressed…” But what does it actually mean and why are we defying the definition? The definition that we overuse and let consume our lives today was coined back in 1936 by a Hungarian endocrinologist Hans Seyle. He deemed that stress is the body’s physical or mental response to a demand or change. A stressor can be anything that is a psychological, physical or social stimulus. Whether that stressor be an illness, studying for an exam or a bad breakup the body reacts the same way; stress is the same whether it be good, bad, chronic or acute.
Taking a toll on the Body
“Every stress leaves an indelible scar, and the organism pays for its survival after a stressful situation by becoming a little older.” – Hans Selye
The effect that stress has on the body can be summed up into three separate stages known as the General Adaptive Syndrome and displays how the human body can infinitely and progressively react to change or stimuli. The three separate stages include alarm phase, resistance phase and the exhaustion phase.
The alarm stage is also known as fight or flight response, because during this stage the nervous system recognizes threat or danger and begins to build up a defense against the stimulus. Physiologically this triggers the hypothalamus that initially prompts the adrenal glands to produce more epinephrine. However, in the long term the glands release cortisol. During the resistance phase, the parasympathetic nervous system is working to return the body to homeostasis. When chronic stress occurs and the body cant reach homeostasis, this is when it begins the phase of exhaustion and the body takes a hit. Because the body has been producing so much excess energy to fight the attacking stressor you reach a point of physical and psychological exhaustion. The immune system changes, cortisol productions rise and soon every organ in the body is susceptible to harm.

“Anything that causes stress endangers life, unless it is met by adequate adaptive responses; conversely, anything that endangers life causes stress and adaptive responses. Adaptability and resistance to stress are fundamental prerequisites for life, and every vital organ and function participates in them.” –Hans Seyle
- Muscle tension can be a reflex when the body feels stress. Long term muscle tension can lead to chronic pain, tension and migraine headaches, muscle atrophy and musculoskeletal conditions.
- Hyperventilation (panic attacks) can sometimes occur because stress makes you breather harder and pushes more rapid breathing.
- The organ typically most commonly affected by stress is the heart. Acute stress can cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure (fight or flight). However chronically this can have serious risks. A combination of high blood pressure, increase heart rate and production of cortisol can lead to risk cardiovascular disease, stroke and heart attack.
- Too much cortisol increases glucose production. This can be especially harmful to individuals with diabetes, high blood pressure or obesity.
- The gastrointestinal system changes significantly. It can range from lack of nutrients due to unhealthy eating habits, vomiting and/or diarrhea or severe stomach pain which could lead to ulcers.
Why should YOU care?

What affects college-aged students most commonly is the effect on intellectual performance and emotional stability. According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, forty million U.S. adults suffer from an anxiety disorder, and 75 percent of them experience their first episode of anxiety by age 22. Stress levels are skyrocketing on college campuses because students are going to drastic measures to “get the A.” Lack of sleep mixed in with increased stress hormones in the body has been shown the cause a direct link to lack of memory and concentration. So in theory, pulling that all nighter for the big exam sounds great but you are more likely to wreak havoc on your nervous system.
If you’re feeling overwhelmed, it’s okay to seek help before your body takes a hit!
Butler University Counseling Services
530 W. 49th Street (HRC, Room 120)
Indianapolis, IN 46208
Phone: (317) 940-9385
Common reasons students utilize the services:
- Relationship issues
- Understanding one’s sexual/gender identity
- Depression
- Eating and body image concerns
- Anxiety
- Self-esteem/self-confidence
- Adjusting to college
- Anger management
- Stress management/coping skills
- Self-care
- Grief and loss
- Alcohol and substance use
- Homesickness
- Sexual assault/trauma
References:
“Living and Thriving-Stress and College Students.” Facts | Anxiety and Depression Association of America. ADAA, n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2015.
Lucille, Holly. “General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) Stages.” General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) Stages. Integrative Therapeutics, LLC, 10 Apr. 2014. Web. 29 Sept. 2015.
Rosch, Paul J. “Hans Selye: Birth of Stress.” The American Institute of Stress. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2015.
Seyle, Hans. “STRESS AND THE GENERAL ADAPTATION SYNDROME.”British Medical Journal (1950): n. pag. Print.
“Stress Effects on the Body.” American Psychological Association, n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2015.
Wu, Joanne. “Rising Stress Levels Alarm Health Educators.” The American Institute of Stress. Stanford Daily News, 29 Feb. 00. Web. 29 Sept. 2015.
Media sources:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=vzrjEP5MOT4http://data.integrativepro.com/images/general-adaptation-syndrome.jpg
http://www.studlife.com/files/2012/04/depression.jpg
http://www.studlife.com/files/2012/04/depression.jpg
The Importance of Vitamin D for Athletes
September 24, 2015
Undoubtedly you have been told to “go outside and get some vitamin D” at some point in your life. The “Sun vitamin” is the only nutrient that we can get from the environment and not just from our diet. As college athletes, we understand the importance of properly fueling our bodies and receiving vitamins our body needs to function best. But do you receive enough Vitamin D? Do you know what vitamin D does? Do you know its affect on athletic performance? If you answered “no” to any of these questions, you’re in the right place. Keep reading to discover the importance of vitamin D!
WHAT IS VITAMIN D?
Greek Olympians were encouraged to train under the sunrays due to its benefits to physical health described by the physician Antyllus. Even then, the benefits of sunshine were apparent on the performance of athletes. Today, we know this is the work of vitamin D. Although vitamin D is considered a “vitamin”-an organic compound in food needed in small amounts for growth and good health-our requirement can be met entirely through synthesis in the skin with sun exposure. Ultraviolet radiation in sunlight converts a precursor located in the skin to vitamin D. From here the new vitamin is sent to the liver where it is converted in to the main storage form. When needed, vitamin D is converted to a hormonal form and driven by parathyroid hormones to work.
VITAMIN D SOURCES
As mentioned earlier, vitamin D can be synthesized upon sun exposure. However, anything that limits amount or quality of sun exposure can compromise vitamin D status. Athletes who live at higher longitudes far form the equator, wear clothing that covers most skin, have darker skin, or have excess body fat will likely not be able to receive their vitamin D requirements via sunlight. The chart below further explains how vitamin D can be limited from the sun
If this is you, don’t panic! The good news is some vitamin D can be obtained through your diet. Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna), mushrooms, yogurt, soy milk, fruit juice, and egg yolks all contain high levels of vitamin D. Work these foods into your diet to replenish you vitamin D stores. Vitamin D can also be supplemented.
HOW MUCH VITAMIN D SHOULD YOU GET?
The US Institute of Medicine Guidelines suggests that people receive 40 nmol/L of vitamin D a day. However, this suggestion continues to rise as many experts believe that 100-250 nmol/L is optimal for human health. Sub-optimal vitamin D is widespread among the general population and athletes. It’s prevalence among athletes varies by season, training locating, sport, and skin color among other factors. Generally, your vitamin D levels are lower during the winter months due to the change in angle of the sun, covering of the skin, and increase in time spent indoors.
At this point, you understand that you may be lacking in vitamin D. But why does this matter? What does vitamin D do for the body and how does it help athletes?
FUNCTIONS OF VITAMIN D
Vitamin D is a genetic modulator to as many as 2,000 genes involved in cellular growth, immune function and protein synthesis. It turns on and off the expression of specific genes to control functions in the body including bone health, skeletal muscle function, and immunity and inflammation.
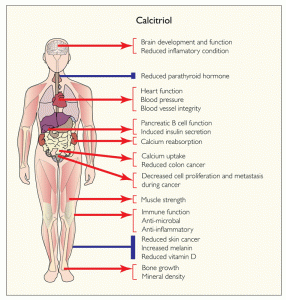
Bone Health: Vitamin D turns on genes that enhance calcium absorption and bone turnover. It is also associated with positive bone mineral density in the hip and lumbar spine of women throughout their life.
Importance for Athletes: Vitamin D is essential for bone health and prevention of bone injury in athletes. Stronger bones mean reduced risk of stress fracture. Athletes who were below 75nmol/L of vitamin D had a risk for stress fractures that was 3.6 times higher than those above this threshold.
Skeletal Muscle Function: Vitamin D turns on the expression of genes that influence muscle growth and differentiation, particularly in fast twitch muscles. It also modulates sarcoplasmic uptake and cell signaling.
Importance for Athletes: muscular pain and weakness are symptoms of vitamin D deficiency. Deficiency induced atrophy of fast twitch muscles, impairs sarcoplasmic calcium uptake, and prolongs the time it takes for muscles to contract and relax.
Immunity and Inflammation: Vitamin D turns on genes in the immune system that help our bodies defend against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. It also increases the production of anti-inflammatory agents in the body.
Because Vitamin D strengthens the immune system, it also helps to prevent cancer. Here is a look at how vitamin D works within the body to do this:
Importance for Athletes: A better immune system means a lower risk of the common cold and influenza. No one can preform at their best when they are sick. The intense training of athletes can lower the ability of the immune system, but vitamin D can help to build back its strength. Finally, anti-inflammatory agents aid with recovery.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Now you know the powers of vitamin D, how it can affect your ability to perform, and how to get it. In order to be the best athlete you can be, your body needs to be in the best condition it can possibly be. A well-rounded diet and lifestyle that includes vitamin D will set you on the track for success!
MAIN POINTS
- Vitamin D may be attained by sensible sun exposure (5-30 min) to arms, legs, and back close to noon several times a week.
- Athletes who cannot obtain sufficient vitamin D from their diet alone should consider supplementing.
- Vitamin D can aid in proper contraction of muscles, prevention of bone injuries like stress fractures, keeping the immune system healthy, and boosting the body’s anti-inflammatory capabilities.
HOW TO GET MORE INFORMATION:
If you are interested in learning more about vitamin D, how to get the proper dosage, and how it can affect your body for the better, contact Butler’s Consultant Dietician Brooke Pearson.
Brooke Pearson
Office: 317-940-6108
Cell: 317-650-8877
bpearso1@butler.edu
There is also a “Vitamin D Calculator” app that allows users to estimate intake of vitamin D and calcium from their food, vitamins, and sun exposure.
REFERENCES:
MEDIA SOURCES:
https://www.mvppt.com/many-older-women-dont-need-vitamin-d-supplements/
http://www.popsugar.com/fitness/Why-Vitamin-D-May-Improve-Athletic-Performance-35004737
https://liveto110.com/103-rethinking-vitamin-d-toxicity-with-morley-robbins/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MtUgi9wZGXU